Acceptance in project management
Acceptance in project management refers to the formal acknowledgment by a client, sponsor, or stakeholder that the project deliverables meet the agreed-upon requirements and are complete. It signifies the transfer of ownership of the deliverables from the project team to the customer or end user. This process is critical to ensuring project success and serves as a milestone that confirms that the objectives of the project have been fulfilled.
Types of Acceptance
- Final Acceptance:
- Occurs at the end of the project when all deliverables are completed, reviewed, and approved.
- Partial Acceptance:
- Applies to specific phases, milestones, or deliverables that are approved incrementally during the project lifecycle.
- Conditional Acceptance:
- Granted when minor defects or issues are identified but do not significantly impact functionality, with an agreement to address these later.
- Provisional Acceptance:
- Temporary acknowledgment for testing or trial purposes, pending final approval.
Importance of Acceptance
- Validates Deliverables:
- Ensures that the project outputs meet the predefined criteria.
- Confirms Completion:
- Marks the official closure of the project or specific phases.
- Establishes Accountability:
- Clearly defines responsibility for the deliverables post-acceptance.
- Facilitates Payment:
- Triggers financial transactions, such as final payments or milestone-based compensation.
- Supports Stakeholder Satisfaction:
- Aligns project outcomes with stakeholder expectations.
- Reduces Disputes:
- Provides a documented record of agreed-upon acceptance criteria and approvals.
Acceptance Criteria
Acceptance Criteria are the specific conditions or standards that a deliverable must meet to be accepted by stakeholders. These criteria are defined during the project planning phase and are used as benchmarks for evaluation.
Characteristics of Effective Acceptance Criteria:
- Clear and Specific:
- Criteria must be unambiguous and easily understood by all parties.
- Measurable:
- Should include quantifiable metrics to assess compliance.
- Relevant:
- Directly related to the deliverable and project objectives.
- Testable:
- Can be verified through inspections, tests, or demonstrations.
Example:
- For a software project, acceptance criteria might include:
- "The system processes 10,000 transactions per minute with 99.99% accuracy."
- "The user interface adheres to the specified design mock-ups and passes usability testing."
Acceptance Process
- Define Acceptance Criteria:
- Collaborate with stakeholders to establish measurable and realistic acceptance criteria during the project planning phase.
- Document Criteria:
- Include acceptance criteria in key project documents like the scope statement, project charter, or requirements specification.
- Review Deliverables:
- Ensure that all deliverables are complete and meet the defined standards before presenting them for acceptance.
- Conduct Testing:
- Perform quality assurance tests, user acceptance tests (UAT), or demonstrations to validate the deliverables.
- Stakeholder Evaluation:
- Allow stakeholders to review the deliverables against the acceptance criteria.
- Obtain Formal Sign-Off:
- Secure written or documented approval from the client, sponsor, or relevant authority to confirm acceptance.
- Address Feedback:
- If the deliverables do not meet the criteria, incorporate feedback, make adjustments, and re-submit for approval.
- Record Acceptance:
- Document the acceptance in project records, including any conditions or reservations.
Tools for Managing Acceptance
- Project Management Software:
- Platforms like Jira, Asana, or Trello can track acceptance criteria and approvals.
- Testing Tools:
- Software like Selenium or TestRail for user acceptance testing (UAT).
- Document Management Systems:
- Tools like SharePoint or Google Workspace for recording and sharing acceptance documents.
- Contract Management Software:
- To link deliverables with contractual acceptance terms.
Challenges in Acceptance
- Unclear Criteria:
- Ambiguities in the acceptance criteria can lead to disagreements.
- Stakeholder Misalignment:
- Conflicting stakeholder expectations may delay acceptance.
- Unrealistic Expectations:
- Criteria that exceed project capabilities or timelines.
- Incomplete Deliverables:
- Submitting incomplete or substandard work for approval.
- Delayed Feedback:
- Prolonged review cycles from stakeholders.
Best Practices for Ensuring Smooth Acceptance
- Collaborative Criteria Development:
- Engage all relevant stakeholders in defining and agreeing on acceptance criteria.
- Regular Reviews:
- Conduct periodic reviews to ensure deliverables align with expectations throughout the project.
- Effective Communication:
- Maintain open and transparent communication channels with stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Training:
- Educate stakeholders on the acceptance process and their roles.
- Proactive Issue Resolution:
- Address potential discrepancies or conflicts early to prevent delays in acceptance.
- Document Everything:
- Keep detailed records of criteria, approvals, and feedback for future reference.
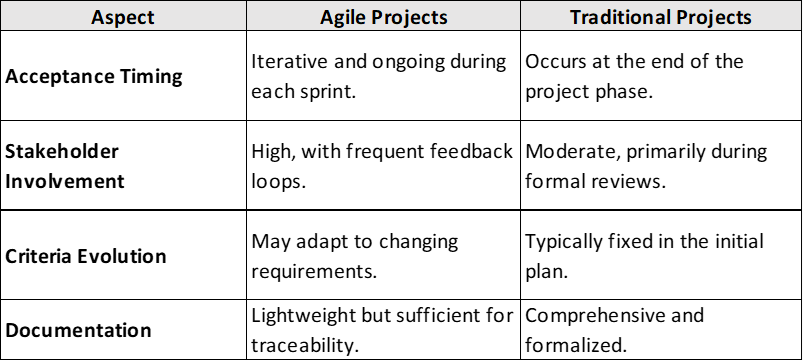
Acceptance in Agile vs. Traditional Project Management
Benefits of Effective Acceptance Management
- Ensures Quality:
- Delivers outputs that meet stakeholder expectations and standards.
- Promotes Trust:
- Builds confidence among stakeholders through transparent processes.
- Minimizes Rework:
- Early identification and resolution of issues reduce the need for corrections later.
- Facilitates Closure:
- Streamlines the project closing phase by providing clear documentation of completed deliverables.
Conclusion
Acceptance is a vital aspect of project management that ensures deliverables meet stakeholder expectations and project objectives. By defining clear acceptance criteria, engaging stakeholders, and maintaining thorough documentation, project managers can achieve successful handoffs, foster stakeholder satisfaction, and enhance overall project outcomes.
Related Terms
Affinity Diagram in Project Management
Affinity Diagram in Project Management An affinity Diagram is a tool used in pro...
Activity List in Project Management
Activity List in Project Management An activity List is a detailed document that...
Annualized Rate of Return (ARR) in Project Management
Annualized Rate of Return (ARR) The Annualized Rate of Return (ARR) is a f...
Alternative Analysis in Project Management
Alternative Analysis in Project Management Alternative Analysis is a decisi...
Agile Project Management (APM)
Agile Project Management (APM) Agile Project Management (APM) is a methodology t...
Activity on Arrow in Project Management
Activity on Arrow in Project Management Activity-on-Arrow (AOA) is a project man...

Featured Links
Contact us
- PMP® Certification Course |
- CAPM Certification Course |
- PMP Certification Training in Mumbai |
- PMP Certification Training in Pune |
- PMP Certification Training in Hyderabad |
- PMP Certification Training in Delhi |
- PMP Certification Training in Chennai |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Ahmedabad |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Bangalore |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Bhubaneswar |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Chandigarh |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Gandhinagar |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Faridabad |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Dombivli |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Coimbatore |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Ghaziabad |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Gurgaon |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Indore |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Jaipur |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Mysore |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Lucknow |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Kolkata |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Kochi |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Nagpur |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Navi Mumbai |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Patna |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Pimpri |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Vadodara |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Trivandrum |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Thane |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Surat |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Noida |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Visakhapatnam |
- PMP® Certification Training Course in Doha |
- PMP Certification Training in New York |
- PMP Certification Training Course in Chicago |
- PMP Certification Training in Austin |
- PMP Certification Training in Minneapolis |
- PMP Certification Training in Atlanta |
- PMP Certification Training in Dallas |
- PMP Certification Training in San Diego |
- CAPM Certification Training in Mumbai |
- CAPM Certification Training in Bangalore |
- CAPM Certification Training in Hyderabad |
- CAPM Certification Training in Delhi |
- CAPM Certification Training in Pune |
- CAPM Certification Training in Chennai |
- CAPM certification Training in Kolkata |
- CAPM certification Training in Gurgaon |
- CAPM certification Training in Noida |
- CAPM Certification Training in Ahmedabad |
- PMI Certified Professional in Managing AI (PMI-CPMAI)™ |
- PMI-RMP - PMI Risk Management Professional |
- PMI-PMOCP - PMI® Project Management Office Certified Professional
- AZ-900: Microsoft Azure Fundamentals |
- AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator |
- AZ-204: Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure |
- AZ-305: Designing Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions |
- AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions |
- AZ-500: Microsoft Azure Security Technologies |
- AI-900: Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals |
- DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals |
- CLF-C02: AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner |
- GCP-FC: Cloud Digital Leader |
- GCP-ACE: Associate Cloud Engineer |
- GCP-PCA: Professional Cloud Architect |
- GCP-PCD: Professional Cloud Developer |
- GCP-PCE: Professional Cloud DevOps Engineer |
- GCP-PDE: Professional Data Engineer |
- GCP-PCNE: Professional Cloud Network Engineer |
- GCP-PCSE: Professional Cloud Security Engineer |
- GCP-ML: Professional Machine Learning Engineer |
- GCP-PBA: Professional Business Intelligence Analyst |
- DP-100: Designing and Implementing a Data Science Solution on Azure |
- DP-203: Data Engineering on Microsoft Azure
- PMP® is a registered mark of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
- CAPM® is a registered mark of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
- PMI-ACP® is a registered mark of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
- Certified ScrumMaster® (CSM) ia a registered trademark of SCRUM ALLIANCE®
- While we strive to ensure that all prices listed on our website are accurate, we reserve the right to modify them at any time without prior notice.
Copyright © Certifyera Consulting Services. All Rights Reserved | Designed and Developed by WebAnaya